Segment Golgi objects per cell
Prerequisites
Before starting this lesson, you should be familiar with:
Learning Objectives
After completing this lesson, learners should be able to:
Segment intracellular objects and assign them to their parent cell
Motivation
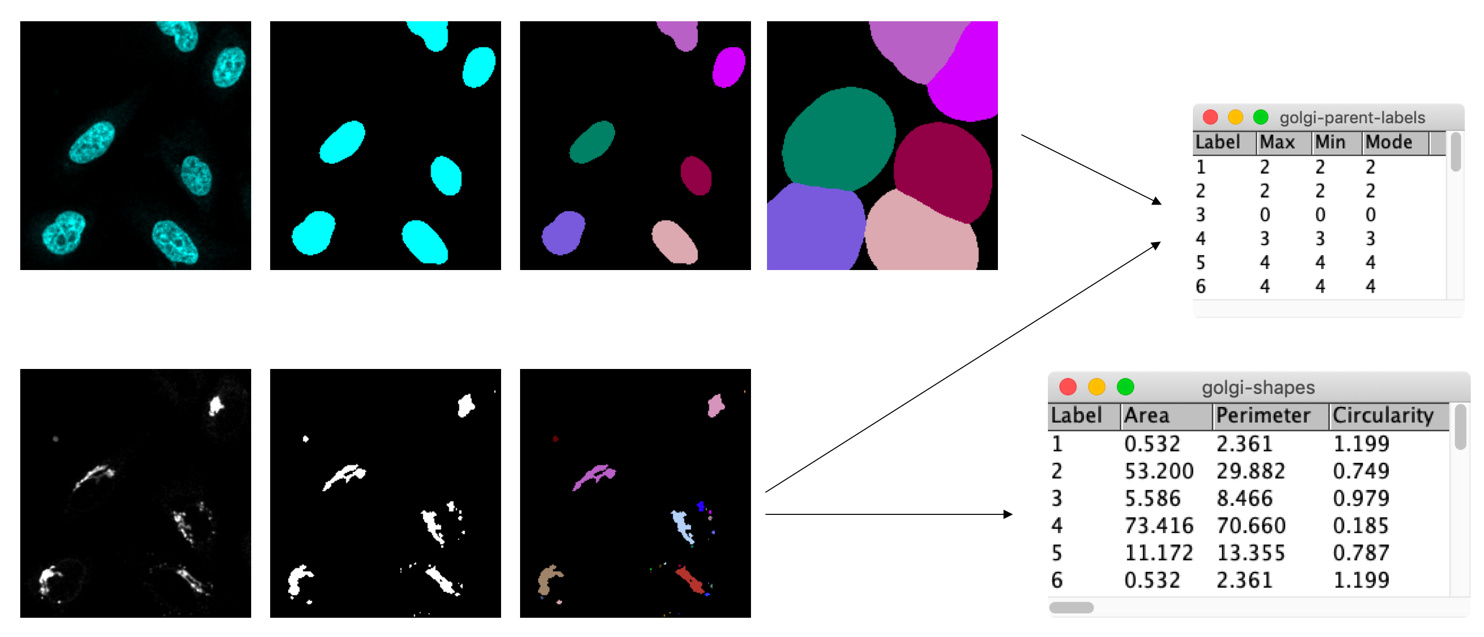
Very often in bioimage analysis one wants to measure the properties of certain intracellular objects (e.g. vesicles) per cell. For example, one may like to measure whether those objects are more frequent or larger in one cell than another. To perform such measurements it is very important to know how to assign (“child”) objects (e.g. vesicles) to (“parent”) objects (e.g. cells).
Concept map
graph TD
N["Nuclei"] --> SN("Segment")
G["Golgi"] --> SG("Segment")
SG --> GL["Golgi (child) label mask"]
SN --> NL["Nuclei (parent) label mask"]
GL -->|assign| NL
Figure
Activities
- Open the image xyc_16bit__nuclei_golgi.tif.
- Segment nuclei and Golgi
- Dilate nuclei to approximate cells
- Assign the Golgi fragments to their parent cell
- Measure the intensity of the child (Golgi) objects in the parent (cell) label mask
- You could, e.g., measure the
min,maxandmodeintensitymin = max: the child object is within one parent objectmin != max: the child object overlaps with multiple parent objectsmode: the label of the parent object that the child object overlaps most with
min = 0: the child object is (partially) located outside of any parent cell
Show activity for:
ImageJ Macro
/** * ImageJ/Fiji Macro * * Required update sites: * - IJPB-Plugins (MorpholibJ) **/ // boilerplate // run("Close All"); run("Options...", "iterations=1 count=1 black"); // parameters // nucleusDilationPixels = 30; // open image open("https://github.com/NEUBIAS/training-resources/raw/master/image_data/xyc_16bit__nuclei_golgi.tif"); rename("input"); // split channels run("Split Channels"); selectWindow("C1-input"); rename("nuclei"); selectWindow("C2-input"); rename("golgi"); // segment nuclei selectWindow("nuclei"); run("Duplicate...", "nuclei-binary"); run("Median...", "radius=5"); run("Auto Threshold", "method=Huang white"); run("Fill Holes"); run("Connected Components Labeling", "connectivity=4 type=[16 bits]"); rename("nuclei-labels"); run("glasbey_on_dark"); // approximate cells by dilation of nuclei run("Dilate Labels", "radius="+nucleusDilationPixels); // run("Remove Border Labels", "left right top bottom"); rename("cells-labels"); run("glasbey_on_dark"); // segment golgi selectWindow("golgi"); run("Duplicate...", "golgi-binary"); run("Gaussian Blur...", "sigma=0.5"); run("Auto Threshold", "method=Huang white"); run("Connected Components Labeling", "connectivity=4 type=[16 bits]"); rename("golgi-labels"); run("glasbey_on_dark"); // measure golgi parent cell index run("Intensity Measurements 2D/3D", "input=cells-labels labels=golgi-labels max min mode"); Table.rename("cells-labels-intensity-measurements", "golgi-parent-labels"); // create image where golgi objects are coloured as parent cells // https://github.com/ijpb/MorphoLibJ/issues/26 // run("Assign Measure to Label"); // measure golgi shape features selectWindow("golgi-labels"); run("Analyze Regions", "area perimeter circularity euler_number equivalent_ellipse ellipse_elong. convexity max._feret geodesic tortuosity max._inscribed_disc average_thickness geodesic_elong."); Table.rename("golgi-labels-Morphometry", "golgi-shapes"); run("Tile");
Assessment
Fill in the blanks
- TODO ___ .
- TODO ___ .
Solution
- TODO
- TODO
Follow-up material
Recommended follow-up modules:
Learn more: